Contents
How Malaria Affect Ethiopia
Malaria: In Ethiopia, almost 75% of the land is malarious and an estimated 51 million (68%) of the
population lives in areas at-risk of malaria. Malaria is still the leading cause of health problem in the
country. In 2004, the disease has been reported as the first cause of illness and death accounting for
15.5% of outpatient visits, 20.4% of admissions and 27% of deaths. The magnitude and periodicity of
malaria epidemics in the country has also been on the rise in the past few years. Some 5,4 million
cases of epidemic malaria cases are expected in 20052
What Cause Malaria and Malaria Effect
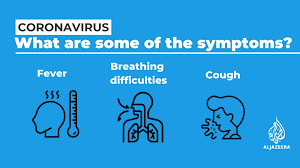
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases it can cause yellow skin, seizures, coma, or death.

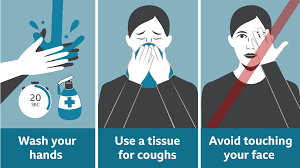
How to Know Malaria in Ethiopia
To diagnose malaria, your doctor will likely review your medical history, conduct a physical exam and order blood tests. Blood tests are the only way to confirm a malaria diagnosis. Certain blood tests can help your doctor by showing:
- The presence of the parasite in the blood, to confirm that you have malaria
- Which type of malaria parasite is causing your symptoms
- If your infection is caused by a parasite resistant to certain drugs
Other blood tests help determine whether the disease is causing any serious complications.
Some blood tests can take several days to complete, while others can produce results in less than 15 minutes.
Treatment
Malaria is treated with prescription drugs to kill the parasite. The types of drugs and the length of treatment will vary, depending on:
- Which type of malaria parasite you have
- The severity of your symptoms
- Your age
- Whether you’re pregnant
Medication
The most common antimalarial drugs include:
- Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs). ACTs are, in many cases, the first line treatment for malaria. There are several different types of ACTs. Examples include artemether-lumefantrine (Coartem) and artesunate-amodiaquine. Each ACT is a combination of two or more drugs that work against the malaria parasite in different ways.
- Chloroquine phosphate. Chloroquine is the preferred treatment for any parasite that is sensitive to the drug. But in many parts of the world, the parasites that cause malaria are resistant to chloroquine, and the drug is no longer an effective treatment.
Other common antimalarial drugs include:
- Combination of atovaquone and proguanil (Malarone)
- Quinine sulfate (Qualaquin) with doxycycline (Vibramycin, Monodox, others)
- Mefloquine
- Primaquine phosphate
.